Wireless EV Charging: Transforming the Future of Electric Vehicles
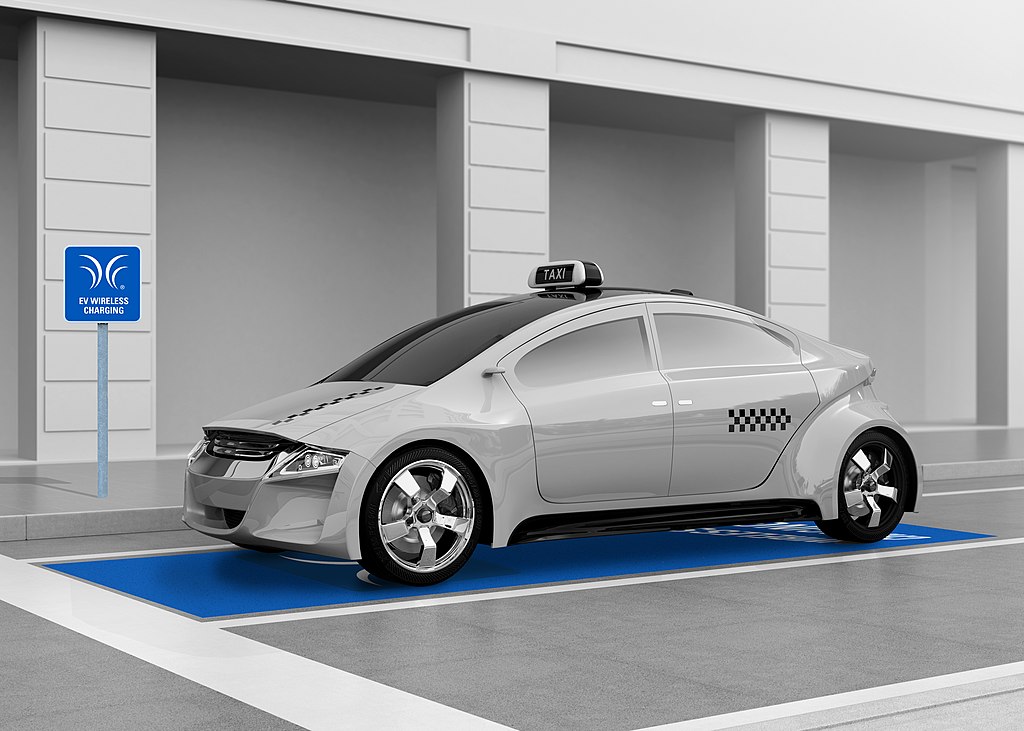

The increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) presents an exciting opportunity to transition toward a sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system.
As the demand for EVs continues to rise, the need for efficient and convenient charging infrastructure becomes paramount. One emerging technology that holds great promise is wireless EV charging. Like with most technologies, mass adoption requires ease of integration into the life of the individual. Read on to learn more about wireless EV charging as an emerging technology, and how it can be taught in the classroom.
What are the Advantages of Wireless EV Charging?
Wireless vehicle charging has several advantages over traditional plug-in charging methods. For one, it eliminates the need for cords and plugs, which can be inconvenient and cumbersome.
It also eliminates the risk of electric shock or other electrical hazards associated with plugging and unplugging a charging cable. Drivers can simply park their vehicle over a wireless charging pad or mat and the battery will begin to recharge automatically.
How Does Wireless EV Charging Work?
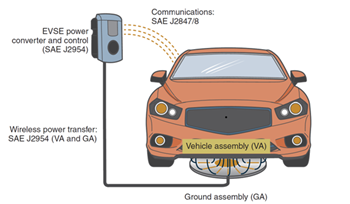
Wireless EV charging, also known as inductive charging or wireless power transfer (WPT), is a method of charging electric vehicles without the need for physical cables or plugs. It relies on the principle of electromagnetic induction to transfer power from a charging pad embedded in the ground to a receiver on the underside of an EV.
This technology utilizes magnetic fields to create a connection between the charging pad and the vehicle, allowing for a seamless and effortless charging experience. While the connection is being made the vehicle will communicate with the Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE), power converter to control the rate of the charge.
Along with controlling the amount of power that is being introduced to the vehicle, information such as temperature of battery cells, level of charge and if there are any current power demands on the vehicle is also present.
All this information will allow the controller to determine the best rate and amount of power the vehicle will require. Automating the charging process will help to make sure the driver will not leave the location without charging the vehicle.
What’s the History of Wireless EV Charging?
The SAE J2954 standard was set on October 22, 2020. This standard, which was updated in August 2022, laid out the charging rates, structure and operational conditions for wireless charging of an EV.
Setting standards for any automotive application allows OEM’s to adopt it as they develop new products for market. The SAE standard codifies the three levels of charging range which are:
- WPT 1 – 3.7 kW
- WPT 2 – 7 kW
- WPT 3 – 11 kW
These levels are based on stationary charging and serve as the start of developing a higher wireless wattage transfer rate.
Along with the WPT transfer wattages, the distance the vehicle’s receiving pad location from the charging pad location is regulated by this standard as well.
At 10in (250mm) of space between the two pads, the transfer efficiency rate is approximately 94 percent. With this high transfer rate, the loss of power to heat or resonance is very low. Inducing power from one power source to another is something that automotive technicians have been working with since the first ignition coil was developed.
Making sure the electric vehicle equipped with WPT is moving the technician to more of an energy technician as they will then have to make sure the vehicle’s charging station in the garage has the proper power output needed to conduct the charging event.
Is Charging While Driving Next?
One of the next steps in wireless evolution is dynamic wireless charging of the vehicle while it is moving down the roadway. Moving the charging of the EV to a dynamic environment is one way to increase mass adoption of electric vehicles throughout the world.
To support this type of “charging roadway” large infrastructure projects must be undertaken. Electreon is one such company that is looking to bring dynamic wireless charging to the roadways of the world.
Electreon is currently developing a pilot wireless charging roadway in Detroit to test the effectiveness of wireless charging throughout the four seasons. They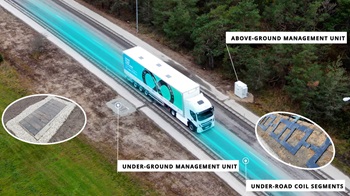 provide this inductive charging by embedding wave coils into the pavement which allows for the vehicle to continue to operate without waiting for a recharge at a charging station. Couple this technology with the increasing fast-charging solid state battery technology and the operational range of an EV will only be limited by the operator stopping for human-related breaks.
provide this inductive charging by embedding wave coils into the pavement which allows for the vehicle to continue to operate without waiting for a recharge at a charging station. Couple this technology with the increasing fast-charging solid state battery technology and the operational range of an EV will only be limited by the operator stopping for human-related breaks.
Weather, like with all technologies, will play a role in the effectiveness of this technology. Working through hot or cold roadway surfaces will affect the rate at which the vehicle can accept a charge from the charging coils.
Throughout the testing process the company will evaluate the best practices to obtain the highest charge rate for the vehicles traveling over the roadway. This trial is a great way to gain proof of concept so the technology can be advanced to a point that it is feasible to be utilized in everyday life.
The size of the interstate system in the United States and other countries will not allow all locations to have this type of technology. Utilizing this type of technology in the right situations, such as metro areas, will have a large impact on traffic flow and will help to minimize the congestion at recharging stations.
As the electric vehicle becomes more integrated into the built environment, the more skill sets built into an automotive curriculum must continue to evolve.
CDX Learning Systems is constantly developing new content, ways to disseminate that content and constantly reevaluating what is the current product offering to make sure it is meeting the needs of the changing landscape in the automotive and diesel training environment.
CDX has a commitment to making sure instructors and students have the relevant training material to further hone their skill sets within the automotive trade. The Light Duty Hybrid and Electric Vehicles title brings this and other technologies into the classroom to keep you up to date on what is currently happening in the mobility industry.
Related Content:- The Hydrogen Fuel Cell Mass Adoption Myth: Should We Teach Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology to Automotive Students?
- 48-Volt Electrical Systems on New ICE and EV Automotive Applications: What Should Your Automotive Program Be Teaching?
- Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Cell Chemistry is Taking Over the Automotive Market: What it Means for Auto Educators
About the Author:
Nicholas Goodnight, PhD is an ASE Master Certified Automotive and Truck Technician and an Instructor at Ivy Tech Community College. With nearly 20 years of industry experience, he brings his passion and expertise to teaching college students the workplace skills they need on the job. For the last several years, Dr. Goodnight has taught in his local community of Fort Wayne and enjoys helping others succeed in their desire to become automotive technicians.